Are you searching for examples of different types of adverbs in English? Here we’re going to explain 7 types of adverbs with adverb examples to help you use them in sentences correctly and expand your English vocabulary.
Types of Adverbs
Full list of adverbs in English.
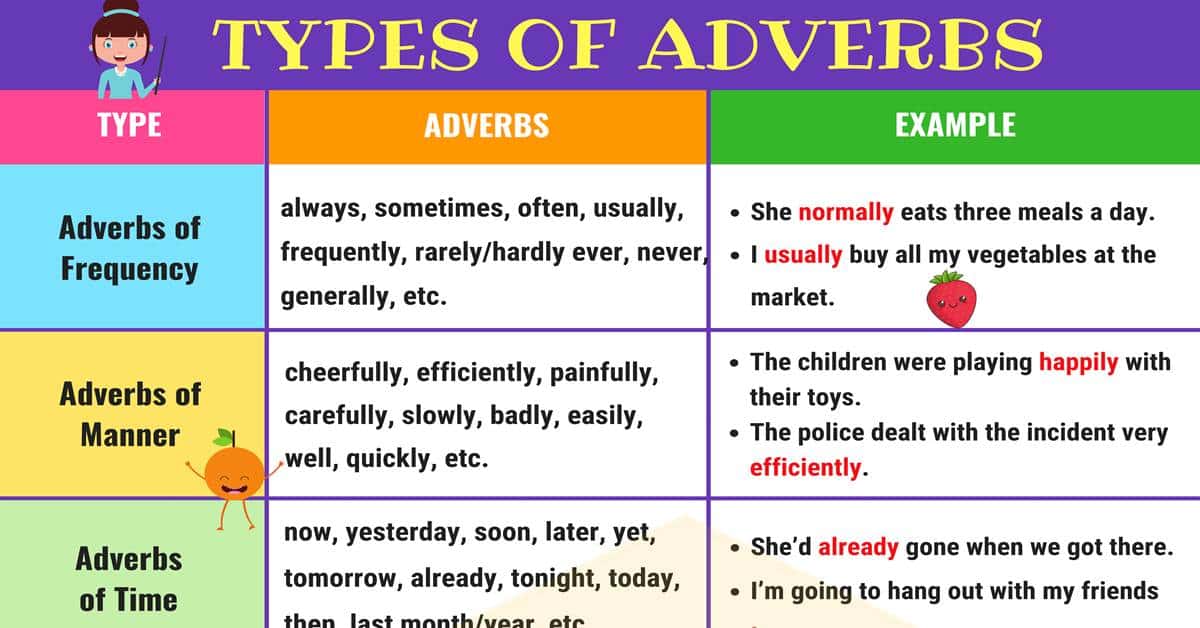
Adverbs of Frequency
We use adverbs of frequency (always, sometimes, often/frequently, normally/generally, usually, occasionally, seldom, rarely/hardly ever, never, etc.) to say how often we do things, or how often things happen.
Adverb Examples:
He always wears a shirt and tie.
She normally eats three meals a day.
I usually buy all my vegetables at the market.
Adverbs of Manner
Adverbs of manner (such as cheerfully, efficiently, painfully, secretly, quietly, peacefully, carefully, slowly, badly, closely, easily, well, fast, quickly, etc. ) tell us how something happens or is done. They are usually placed either after the main verb or after the object.
Adverb Examples:
The children were playing happily with their toys.
The police dealt with the incident very efficiently.
Birds sang cheerfully in the trees.
Adverbs of Time
Time adverbs (now, yesterday, soon, later, tomorrow, yet, already, tonight, today, then, last month/year,…) tell us about when something happens.
Adverb Examples:
I’m going to hang out with my friends tomorrow.
I’ll call you from home later.
She’d already gone when we got there.
Adverbs of Place
Place adverbs (off, above, abroad, far, on, away, back, here, out, outside, backwards, behind, in, below, down, indoors, downstairs, inside, nearby, near, over, there, towards, under, up, upstairs, where, everywhere, elsewhere, anywhere, nowhere, somewhere…) tell us about where something happens or where something is. They are placed after the main verbs of after the clause that they modify.
Examples of Adverbs:
His children go everywhere with him.
She started work here last May.
Let’s open the box and see what’s inside it.
Adverbs of Degree
Degree adverbs (quite, fairly, too, enormously, entirely, very, extremely, rather, almost, absolutely, just, barely, completely, enough, deeply, enormously, fully, greatly, hardly, incredibly, practically, scarcely, barely, somewhat, terribly, virtually, …) express degrees of qualities, properties, states, conditions and relations.
Examples of Adverbs:
He was quite agreeable to accepting the plan.
I’m not absolutely certain I posted it.
The building was completely destroyed.
Adverbs of Evaluation
Evaluative adverbs are used by the speaker to comment or give an opinion on something. Evaluative adverbs modify the entire clause.
There are several types of adverbs of evaluation, which can be classified according to their function. Some give information about how certain we consider something to be, others express our attitude (negative or positive) about something, while others are used to pass judgement on someone’s actions. Some of the most common evaluative adverbs for each function are listed below:
Adverbs of Certainty
(Types of adverbs)
We can use the evaluative adverbs to state how certain we are about something, such as apparently, clearly, definitely, doubtfully, doubtlessly, obviously, presumably, probably, undoubtedly, etc.
Adverbs Examples:
David is clearly unhappy to be here.
Apparently, we’re going to have to work harder.
Obviously, we don’t want to spend too much money.
Adverbs of Attitude
(Types of adverbs)
We can use the evaluative adverbs to make our attitude about something clear, such as astonishingly, frankly, fortunately, honestly, hopefully, interestingly, luckily, sadly, seriously, surprisingly, unbelievably, etc.
Examples:
Hopefully, he will reach the top.
Honestly, I could’t eat another bite.
Frankly, I think the Internet is overrated.
Adverbs of Judgement
(Types of adverbs)
We can use the evaluative adverbs to make judgments about someone’s actions, including our own, such as bravely, carelessly, fairly, foolishly, generously, kindly, rightly, spitefully, stupidly, unfairly, wisely, wrongly, etc.
Examples:
She kindly lent me her bicycle.
The jacket is very generously cut.
I carelessly broke the glass.
Conjunctive Adverbs List (Linking Adverbs List)
Linking adverbs are adverbs that are used to link ideas or clauses in spoken discourse or written text. (Such as accordingly, besides, comparatively, conversely, equally, further, hence, in comparison, incidentally, namely, next, now, rather, undoubtedly, additionally, anyway, certainly, elsewhere, finally, in addition, in contrast, indeed, moreover, nonetheless, similarly, subsequently, thereafter, yet, also, meanwhile, consequently, nevertheless, finally, next, furthermore, otherwise, however, still, indeed, then, instead, therefore, likewise, thus, etc). They could also be called conjunctive adverbs in so far as they perform the same sort of function as conjunctions.
Examples:
Furthermore, they had not consulted with her.
Some of the laws were contradictory. Accordingly, measures were taken to clarify them.
I don’t want to go; besides, I’m too tired.
















0 Comments