What is a pronoun? One of the most important forms of grammar in the English language is the pronoun. This is something that you will come across very frequently when studying the language and it is important that you are aware of what a pronoun is, how it is used and where it fits into a sentence. In this article, we are going to be taking a look at how pronouns work and what they are used for, this will be intertwined with some examples so that we can gain a better understanding of their function.
Pronoun
What Is A Pronoun?
What is a pronoun in English grammar? One of the nine parts of speech in the English language is the pronoun. A pronoun is a word that substitutes for a noun or noun phrase. Pronouns help keep our writing varied. Without pronouns, we would have to constantly repeat the same noun over and over again to tell a story. For example, if we wanted to write a story about Mary we would constantly have to repeat her name.
- Mary went to the store to buy a shirt. Mary picked up a blue shirt to go with Mary’s jacket.
You could use alternative appellations to make the text more varied. However, this could confuse the reader. You reader may think that the two names you use are different entities entirely. For this reason, we use pronouns for noun substitutions.
- Mary went to the store to buy a shirt. She picked up a blue shirt to go with her jacket.
Using she and her makes it clear that Mary is being referenced. There is no ambiguity.
Pronoun Examples
In the most simple terms, a pronoun is a word which takes the position of a noun. One of the most commonly recognised forms of the pronoun are names of people, for example, John, Jill, Mary or Peter. However, a pronoun could also be one of the following words:
- He/she
- It
- They
- Me
- Himself
- Somebody/everybody/anybody
- Many
- Each
- Few
- Whoever/who
A pronoun is used instead of a noun or noun phrase in a sentence. A pronoun may take place of the name of a person, place or thing.
Pronoun examples: I, me, we, they, you, he, she, it, yours, himself, ourselves, its, my, that, this, those, us, who, whom…
There are many more examples of pronouns, and you might think of them as pointing towards possession. As we mentioned, the pronoun is used as a way of replacing a noun, take a look at the following sentence:
- The couch is large, the cupboard is heavy.
There is no need to use the word couch in the second part of the sentence, therefore it could be replaced with a pronoun now that we recognise what item is being talked about, take a look at the modified sentence which uses the pronoun it.
- The couch is large, it is heavy.
Pronouns List
We see pronouns in the English language every day. They help to make our texts more interesting. To understand how to use a pronoun properly you need to be familiar with the differences between different types of pronouns.
Below find a list of common pronouns and the main categories in which they belong.
- Reflexive: myself, yourself, himself, herself, itself, themselves, yourselves, and ourselves
- Personal: subjective (he/ she, I, you and they); objective (me, you, her/ him, it, them, and us); possessive( hers/his, mine, yours, its, ours, and theirs)
- Relative: whom, that, who, and which
- Indefinite: all, any, anybody, everybody, everyone, another
- Demonstrative: this, that, these, and those
- Interrogative: who, what which, and what
- Intensive: myself, yourself, himself, herself, itself, themselves, yourselves, and ourselves
Types of Pronouns and List of Pronouns – Image 1
Antecedent
An antecedent, a noun or noun phrase, provides context for a pronoun. The antecedent allows readers to know what a particular pronoun is referencing. For example, it can refer to many different nouns: a garden hose, a shed, or almost any other noun you may need to mention.
You will find the antecedents in the examples below italicized. The pronouns are in bold.
- Mary decided that she would drive down to visit her grandmother.
- The sun smiled while it ducked under the clouds.
Sometimes a writer will not explicitly need to include an antecedent. If the context of a sentence remains clear an antecedent is not necessary. If you know who is speaking, the pronouns I, me, and you can be clearly understood.
Technically, you can place a pronoun before an antecedent. Most people choose not to do this because it can confuse the reader.
- I love it! My beautiful yellow jacket makes me happy.
Types of Pronouns (with Pronoun Examples)
English Pronouns can be divided into several categories: personal, indefinite, reflexive, reciprocal, possessive, demonstrative, interrogative, reciprocal and relative.
We briefly discussed some of the different words that are classed as pronouns, however there are also different types of pronoun. Most often, pronouns fall into one of nine categories. We will now take a look at each of these.
Personal Pronouns
This type of pronoun is used to refer to a person, in this category you will see words such as I, we, you, they, he, she, …
- I have green eyes.
- They are coming to my house.
- You are my friend.
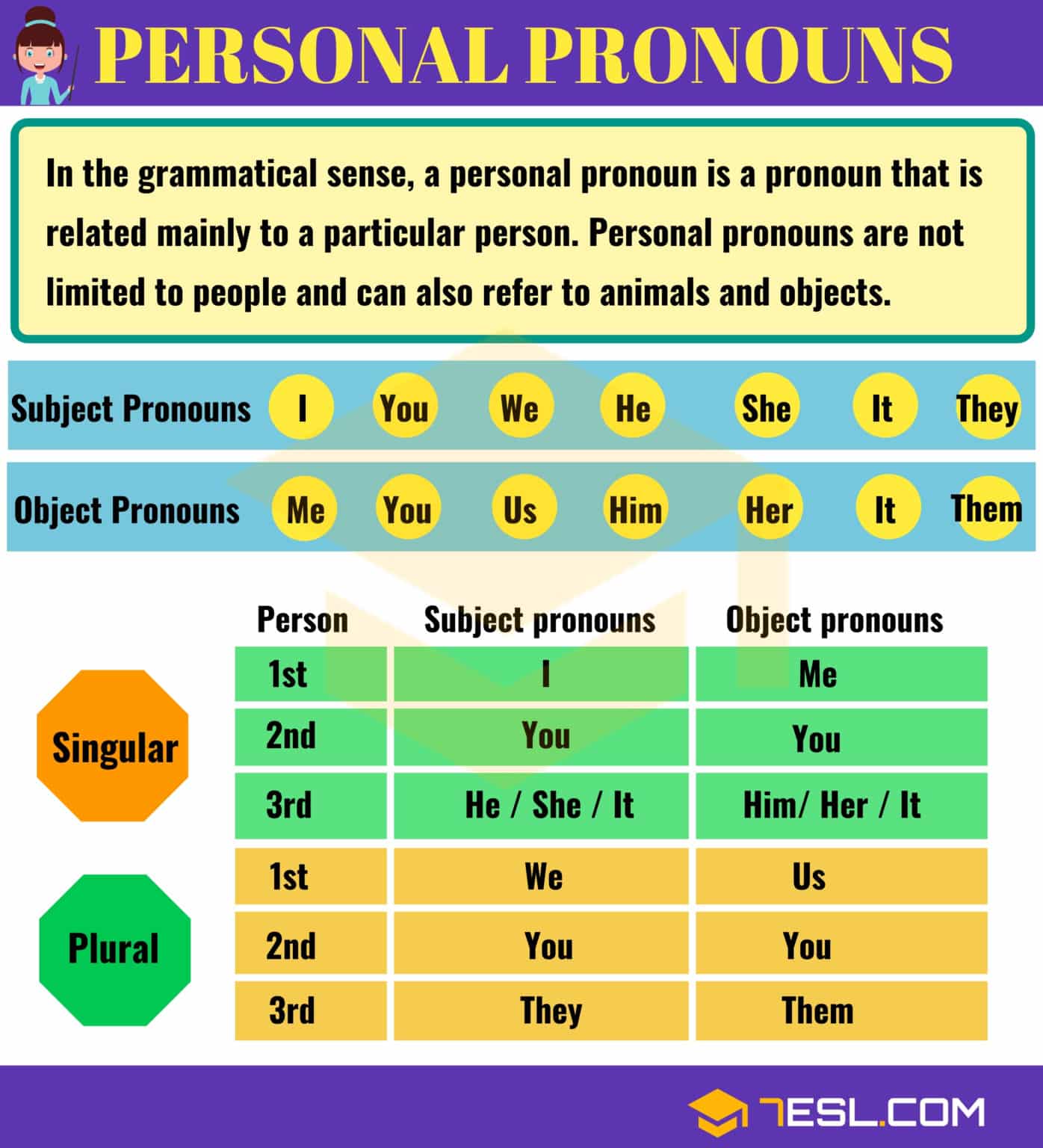
There are two types of personal pronouns: subject and object.
When the person or thing is the subject of the sentence, subject pronouns are used.
Subject pronoun list: I, you, he, she, it, we, they.
Subject pronoun examples:
- I like to watch TV, but he does not.
- You cannot judge a tree by its bark.
- She struck him on the nose.
- He studies hard to pass the exam.
Object pronouns are used when the person or thing is the object of the sentence.
Object pronoun list: me, you, him, her, it, us, you, them.
Examples:
- Sophia likes me but not him.
- John will call you soon.
- Don’t tell her the truth.
- I helped him pull his boots off.
Reflexive Pronouns
The reflexive pronoun will end in -self or -selves and is used in reference to another pronoun. Words within the category are himself, herself, themselves, yourself/ves, myself, itself.
- He takes care of himself.
- She can do it by herself.
- You could travel by yourself.
In English, reflexive pronouns are used when a person or thing acts on itself.
Reflexive pronoun list: myself, yourself, himself, herself, itself, ourselves, yourselves, themselves.
Examples:
- She tried it herself.
- Tom hurt himself.
In English they all end in –self or –selves and must refer to a noun phrase elsewhere in the same clause.
Possessive Pronouns
In English, possessive pronouns are used to indicate possession or ownership. They are: mine, yours, his, hers, ours, yours, theirs.
Possessive pronoun list: mine, yours, his, hers, ours, yours, theirs.
Examples:
- Do you see that woman over there? Her dog is very friendly.
- Is that your house? No, ours is the one beside it.
- his is my laptop. It’s mine.
- These books are mine, not yours.
- This is my brother ‘s book. It’s his.
Demonstrative Pronouns
This type of pronoun is used to indicate something, the words in the category are these, those, that, this.
- These are the shoes that I am going to wear.
- He likes the green flowers but he prefers those red ones over there.
- I would like that one.
The demonstrative pronouns are the same words as the demonstrative adjectives (this, that, these, and those). They often distinguish their targets by pointing or some other indication of position. They can be either near or far in distance or time, specifically.
Demonstrative pronoun list: this, that, these, those.
Pronoun examples:
- This is an enormous field.
- Can you see that?
- These are delicious cookies.
Indefinite Pronouns
The indefinite pronoun is used to talk about something which is not specific. Words in the category are some, all, few, none, either, one, nobody, both, each, anyone, several etc.
- Nobody is going to the party.
- There are several people in my class.
- I like both of these photos.
An indefinite pronoun is a pronoun that refers to non-specific beings, objects, or places. Indefinite Pronouns can also function as other parts of speech too, depending on context.
Indefinite Pronoun List: another, anybody/ anyone, anything, each, either, enough, everybody/ everyone, everything,…
Pronoun examples:
- I don’t want anyone to see it.
- Is there anything in that box?
- You can’t blame him for everything.
- Each company is fighting to protect its own commercial interests.
- Much has happened since we met.
- No one can cope with her in English.
Relative Pronouns
This type of pronoun can be used as a way of giving additional information within a sentence, pronouns in this category are that, who, which, whom…
- This is my brother who lives in New Zealand.
- This is the ball that my dog likes best.
A relative pronoun is a pronoun that relates to the word that it modifies and is not specific. In English, relative pronouns are who, whom, which, whose, and that. They refer back to people or things previously mentioned, and they are used in relative clauses.
Relative pronoun list: who, whom, which, whose, that.
Pronoun examples:
- The woman who called yesterday wants to buy the house.
- Now they were driving by the houses which Andy had described.
- She is an artist whose work I really admire.
- The author whom you criticized in your review has written a letter in reply.
Intensive Pronouns
The intensive pronoun is used as a reference to another pronoun or noun in the same sentence as a way of emphasizing it.
- The dog caught the ball itself.
- Sarah cooks dinner herself.
- I eat my candy myself.
Interrogative Pronouns
An interrogative pronoun is used in a question, the words within the category are who, which, where, how and what.
- How many apples do you have?
- Which way is the hotel?
- Is that where the chair goes?
Reciprocal Pronouns
The reciprocal pronoun is used to show an action or feeling which is reciprocated, words in this category are one another and each other.
- They are happy with each other.
- The two friends really care about one another.
List of Pronouns
Learn the list of all pronouns in English with different types.
1) Personal pronoun list
- Subject pronouns: I, you, he, she, it, we, they.
- Object pronouns: me, you, him, her, it, us, you, them.
2) Demonstrative pronoun list: this, that, these, those.
3) Reflexive pronoun list: myself, yourself, himself, herself, itself, ourselves, yourselves, themselves.
4) Intensive pronoun list: myself, yourself, himself, herself, itself, ourselves, yourselves, themselves.
5) Possessive pronoun list: mine, yours, his, hers, ours, yours, theirs.
6) Relative pronoun list: who, whom, which, whose, that.
7) Indefinite pronoun list: another, anybody/ anyone, anything, each, either, enough, everybody/ everyone, everything, less, little, much, neither, nobody/ no-one, nothing, one, other, somebody/ someone, something, both, few, fewer, many, others, several, all, any, more, most, none, some, such.
8) Interrogative Pronoun List: who, whom, which, what, whose, whoever, whatever, whichever, whomever.
Pronoun Rules
As with all types of grammar, there are rules surrounding the use of the pronoun. Let’s take a look at these now.
1) If the pronoun is being used as a subject it is known as a subject pronoun and often appears at the beginning of a sentence, although this is not always the case. An example of this would be She went to the shop.
The words he, I, she, we, whoever, they, it etc are all subject pronouns,
2) Secondly, a subject pronoun can be used if they are renaming the sentence subject, in this case, they always come after to be verbs, these might be verbs such as were, am, are, is, etc. An example of this would be That is she or This is him talking.
3) Another rule is that if the word who is being used as a pronoun to refer to a person, it will take the form of the verb to which that person corresponds, this might sound strange as this rule is not always followed but an example might look like this It is I who am going to town.
4) An object pronouns is used to refer to the object of a sentence. Object pronouns might include the words him, me, her, us, them, etc. An example of this might be Sarah watched her. In this example. her is the object of the verb watched.
5) When a possessive pronoun is used, the use of an apostrophe is never required.
6) When using the pronouns which, that, and who you should use either a singular or plural verb depending on what the pronoun is referring to. For example, look at the following sentence.
- John is one of those men who likes fishing.
- John and Bob are two of these men who like fishing.
You can see that the verb like has been modified to become plural when the pronoun who refers to two people as opposed to one.
Gender Pronouns
Gender pronouns exist in a binary system: male or female. In this system, he/him/his or she/her/hers are pronouns used to delineate gender. These pronouns occur in the 3rd person singular.
Who vs. Whom (Subject and Object Pronouns)
Who and whom are two relative pronouns. These relative pronouns cause the most confusion among English language writers. It is simple to understand which one to use in a sentence. You just need to remember who is a subject pronoun and whom is an object pronoun.
Who functions like other subject pronouns: I, we, she/he, and they. In contrast, whom works like other object pronouns: him, us, me, her, and them. Generally, people do not get bewildered by the object use of pronouns. Object pronouns come after a modifying verb or preposition. For this reason, they are easier to identify. For example:
- Please give the girl to me.
- The woman bought them a cat.
The examples above show how the prepositions/verbs (bolded) precedes the object pronouns (italicized). The personal pronoun whom deviates from this sequence. In this case, the object pronoun whom comes before the verb or preposition that seeks to modify it. For example:
- Whom should I direct my anger towards?
- The man was as bitter as the twins, whom he described as sore losers.
You can use an alternative personal pronoun in place of who or whom to decipher the correct word to use. If the sentence works with an object pronoun you use whom. If it works with a subject pronoun then who is the word needed. In the first example, you can substitute her. The subject pronoun she would make no sense.
- Correct: Should I direct my anger towards her?
- Incorrect: Should I direct my anger towards she.
Common Mistakes with Pronouns
Choosing a singular pronoun for a plural noun
The problem many people have with pronouns is choosing the right form to replace the noun. Sometimes people will replace a singular noun with a plural pronoun or a plural noun with a singular pronoun.
- Incorrect: The guest needs their own towel.
- Correct: The guest needs his/her own towel.
Object and subject pronoun misuse
Problems arise when people have to choose between the subject and object cases. You need to know which case to use when replacing a noun. Otherwise, your sentence will not be grammatically correct.
Subject pronouns represent a noun performing an action. In contrast, an object receives the action performed by the subject.
- Incorrect: Between you and I, miracles happen.
- Correct: Between you and me, miracles happen.
You would use the object case because it is part of a prepositional phrase.
Incorrect reflexive pronoun use
People often use reflexive pronouns wrong when they try to write formally. You use reflective pronouns when the subject is also the object of a sentence. For example, you would not write Mary hurt Mary. Instead, you would write Mary hurt herself. You would use the reflexive pronoun herself instead of Mary.
You can also use reflective pronouns for emphasis; however, it not commonly used. For example, I myself went to the store. This example highlights the fact the person when to the store alone.
Pronouns Examples | Picture
Types of Pronouns and List of Pronouns – Image 2
Conclusion
Pronouns are words which are used as a replacement for a noun and are commonly seen throughout the English language. There are various types of pronouns and certain rules that must be followed in order to create a grammatically correct sentence.
Pronoun Quiz Exercises
Pronoun Quiz #1
Select the correct pronoun in each question.
- Piper asked ____ friend to pass the salt. her or she
- My aunt needs ____ tires changed. her or she
- My cousin and ____ went to the zoo. I or me
- Did the dogs find ____? we or us
- The girls had ____ tonsils removed. her or their
- Where did ____ go? you or us
- When will ______ visit the cabin? they or them
- After school, ______ went the doctor. her or she
Pronoun Quiz # 2
Circle the pronouns in the sentences below.
- Mary went to the store and she bought a duck.
- My niece brought her blanket to the living room.
- They went to the cabin to help us.
- The boys selected their respective guitars.
- They visited his father’s old stomping grounds.










0 Comments