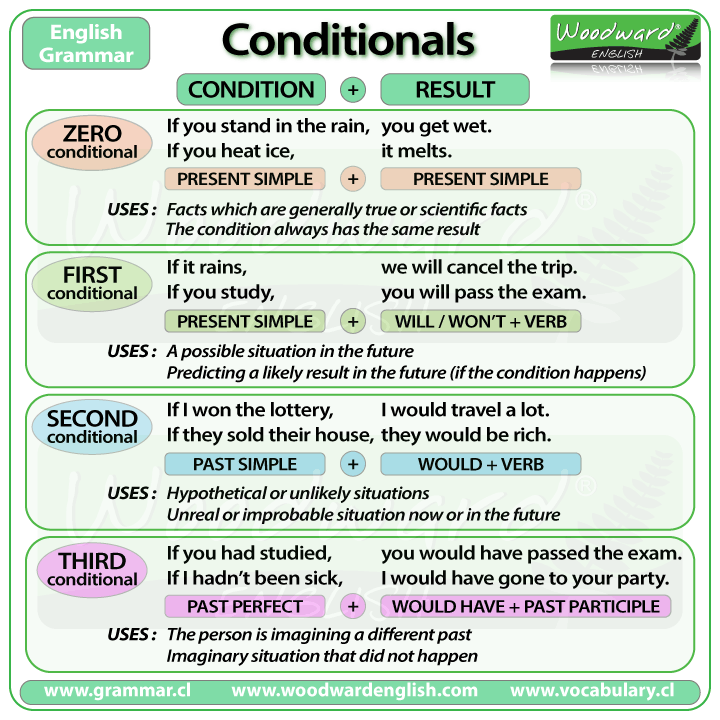
Conditional sentences have two parts: the if-clause and the main clause.
Example sentence: If it rains, I will cancel the trip.
If it rains is the if-clause and I will cancel the trip is the main clause.
The IF-clause introduces a condition. The main clause is the result of that condition.
What happens in the main clause is conditional to what happens in the if-clause. In other words the main clause only happens when the events in the if-clause happen.
As you can see, each type of conditional has its own combination of tense used in the if-clause and tense used the main clause. These different pairings of tenses give each type of conditional its own meaning.
Other types of conditional clauses
Now, these four types of conditional clauses are the traditional ones though there are OTHER types of conditional clauses.
IF + PRESENT SIMPLE, ...+ IMPERATIVE
We use the imperative to give instructions of advice.
- If you see John, tell him he needs to come to my office.
- If you travel abroad, remember your passport
- If you go to Australia, send me a postcard.
- If you go to the supermarket, bring back some milk.
- If Mike comes, call me.
- If you drink, don't drive.
The highlighted words are in the imperative. These sentences are similar to saying: If the first condition happens, you must do this (in the second/imperative clause).








0 Comments